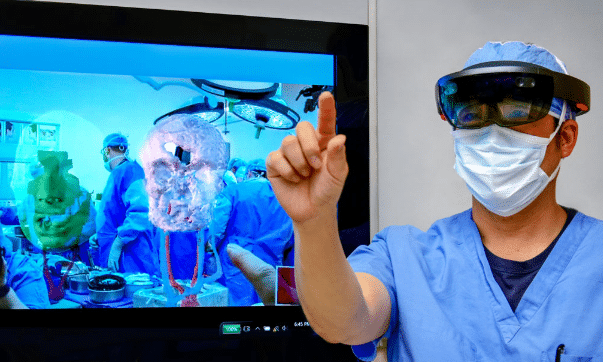
For several years, augmented reality (AR) has become a landmark in the evolution of modern medicine.
In the beginning there were applications for viewing diagnostic images in 3D.
Today, new AR technologies are increasingly being used to improve learning and clinical practice, opening new frontiers to medical education and expanding the knowledge of the profession.
Let’s find out the main uses by pare of health professionals.
Sommario
- 1 Increased health care: the treatment of pain
- 2 The Vostars example: improving surgical performance
- 3 What is augmented reality: difference between pass-through and see-through
- 4 AR and medical education
- 5 AR and cranio-maxillofacial and plastic surgery
- 6 AR and therapies against liver cancer
- 7 AR and medicine in Italy: orthopedic surgery, vascular surgery, and oncology
- 8 AR and Cardiology
- 9 AR and dentistry
- 10 AR and medicine: sharing standards
- 11 REQUEST A NO-OBLIGATION DEMO
- 12 Fastbrain for public administration
- 13 About Fastbrain and why to choose it
- 14 Contact us for a free consultation
Increased health care: the treatment of pain
Augmented health, digital health, are some of the definitions that include augmented reality (AR) technologies and the metaverse in general on medical and generalist titles.
The field of what was once referred to as “telemedicine” has made enormous strides and continues its evolution toward systems that are increasingly accurate, easy to use, and affordable in cost.
From treating pain and stress to reducing anxiety, experimentation in this area is extensive both overseas and in Europe.
One example is a trial that achieved, through AR, a 90% reduction in sedation at Fatebenefratelli in Milan.
The hospital team with vascular access specialist Dr Gianuario Sanna published the study with encouraging results in The Journal of Vascular Access.
The study is also currently in full swing at Buzzi Hospital, Besta Neurological Institute in Milan, Gaslini Institute in Genoa, Regina Margherita Hospital in Turin, and Spedali Civili Hospital in Brescia, with the aim of reducing both pharmacological sedation and operational costs and side effects for patients.
One of the trials is based on virtual reality gaming software designed to help young cancer patients cope with therapy while collecting data useful to the hospital in tailoring therapy to the patient’s needs.
Children are immersed in a stimulating fantasy scenario that can calm stress and anxiety, helping to relax them.
Its application, coupled with vascular access practices via placement of Picc, a venous catheter inserted at arm level, reduces clinical anxiety and pain perception, offering an alternative to the administration of sedative drugs.
The Vostars example: improving surgical performance
From therapeutic care to surgical practice, augmented reality is rapidly evolving toward increasingly advanced, useful, and effective models.
One example is provided by the Vostars (Video and Optical See Through Augmented Reality surgical Systems) project, which gave birth to a special visor that can improve surgical performance.
Following the project is a team of European researchers coordinated by the Department of Information Engineering at the University of Pisa.
Already used in six surgeries, the pilot operation, at Policlinico Universitario S. Orsola in Bologna, was amaxillofacial surgery, repositioning a patient’s maxilla and mandible to restore bite function.
How do visors work in surgery?
Depending on the context, the operation changes. From superimposing three-dimensional maps of the patient on the endoscope (endoscopic surgery) to projecting the information directly in front of the surgeon’s eyes via a viewer.
The result is an ergonomic and precise view of the surgical plane.
The project is funded by the European Community and enables pinpoint accuracy during surgeries, bringing crucial information in real time, such as the patient’s blood pressure and heart rate.
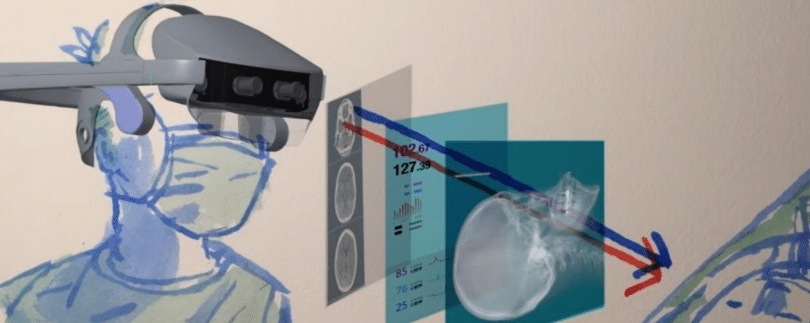
Image source: https://www.scienzedellavita.it/it/meetthelifesciences/7956-condotta-la-prima-operazione-guidata-dalla-realta-aumentata
As evidenced by thearticle “Augmented Reality in Medicine: Systematic and Bibliographic Review” on 1309 publications from databases such as PubMed and Scopus in the period from 2012 to 2017 alone, the technology has developed mainly on visualization techniques, with increased interest in AR applications in medicine.
What is augmented reality: difference between pass-through and see-through
Augmented reality allows virtual elements, data and fundamental information to be superimposed on the user’s perspective of the surrounding environment.
This technology can be further divided into two categories:
- “AR pass-through,” in which real-world images are captured by a camera and displayed on the screen for the user (e.g., in AR applications for smartphones or on some virtual reality viewers);
- “AR see-through,” in which the real world is seen directly through the visor of a virtual reality visor, with virtual elements superimposed simultaneously. *
AR and medical education
The study Augmented Reality in Medical Education: A Mixed Methods Feasibility Study explores the application of augmented reality (AR) inmedical education, with a focus on medical student training to assess the applicability of AR in pre-graduate and post-graduate medical education.
The research involved 15 students, with remote simulation for ICU airway management using Microsoft HoloLens technology, with positive and promising feedback in four key themes: conceptual visualization for learning, accessibility, variable immersion, and future applications.
AR and cranio-maxillofacial and plastic surgery
Thescientific article Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality in Plastic and Craniomaxillofacial Surgery: A Scoping Review reviewed publications between 2015 and 2022 focusing on the use of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) in plastic and cranio-maxillofacial surgery.
Most studies have validated theaccuracy of virtual platforms at various levels.
In plastic and cranio-maxillofacial surgery, VR and AR have been used mainly as preoperative planning tools, but also during surgery.
AR and therapies against liver cancer
Other uses of AR in clinical medicine are highlighted in thearticle Cleveland Clinic Using Augmented Reality to Enhance Liver Cancer Therapy.
At the Cleveland Clinic, AR has been used to improve liver cancer therapies and other surgeries by visualizing 3D holograms of patients during preoperative planning and the performance of surgical procedures.
The efficacy of the technology has been shown to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of minimally invasive thermal therapy (microwave ablation) in destroying liver tumors by providing the physician with a kind of “X-ray vision” to visualize the path to the tumor more precisely.
AR and medicine in Italy: orthopedic surgery, vascular surgery, and oncology
At the San Francesco Clinic in Verona, the first orthopedic wrist surgery in Italy using AR was conducted.
In the clinic, which is already known for the use of robotics in prosthetic surgery, two operations were performed with the support of augmented reality viewers and 3D images of the operated segments: the reconstruction of a major wrist ligament and the treatment of the rhizoarthrosis, a arthrotic pathology common, with the implantation of a trapeziometacarpal prosthesis.
Enrico Carità, one of the orthopedic surgeons who performed the surgeries, said:
“Granted that the level of perfection depends on the surgical gesture, being able to compare virtual and real images in real time helps to even better achieve the goals set during surgery planning, thus ensuring greater accuracy.”
Combining virtual images with real ones offers benefits beyond surgical practice, embracing the educational and caregiving side.
It can foster distance education and communication among experts, giving the opportunity to interact without the need for physical presence, and predictions of the nearer future see a virtuous combination of AR, orthopedic engineering, and robotics (Charity).
Some advantages:
-Abilityto connect remotely with experienced colleagues to share clinical and preoperative images, technical decisions, and surgical indications;
– Use of AR also in fields such as vascular surgery, which involves visualization of angiographic images, which is essential for complex interventions on the vascular system;
– In oncology, three-dimensional visualization of the masses to be removed is crucial to the effectiveness of the surgery.
On the GVM (Gruppo Ospedaliero Italiano) website, in thearticle Preoperative study with augmented reality: The patient’s heart in a 3D hologram, an article was published highlighting the importance of preoperative study for successful surgery.
AR and Cardiology
The interventional cardiology team at Maria Cecilia Hospital for the first time in Italy used augmented reality for 3D holographic reconstruction of the heart and heart valves.
The software created is interactive and allows the image to be manipulated without additional hardware, zoomed in to examine anatomical details, and the surgical gesture simulated with augmented reality reproduced instruments.
Key benefits include precise evaluation of surgery options and detailed preoperative simulation.
An innovative technology called “Advanced 3D-Based Teaching Models in Congenital Cardiovascular Disease” has been developed at the University of Padua that is revolutionizing the teaching approach of medical students in the study of the heart.
The tool, using augmented reality, three-dimensionally reconstructs the heart and its congenital defects, allowing students to explore in detail or the organ directly from their smartphones.
Benefits offered:
- A better understanding of congenital heart disease with three-dimensional digital models based on different radiological imaging techniques.
- A virtual library of congenital heart disease cases for educational and clinical purposes,
- Interaction with 3D models of pathological hearts through an Android and iOS app using augmented reality.
- A potential transformation of the way medicine is taught, making learning more interactive and effective, especially in the field of congenital heart disease.
AR and dentistry
In the dental field, thetelecooperation application of Genovese dentist Luigi Rubino emerges.
It is an augmented reality system based on a special visor that can “guide the operator with hand gestures or signs superimposed on the display (HMD) he wears; that is, both can physically show and visualize without latency where to make an incision or use physical gestures to illustrate the technique.” (Ruby)
The potential of the tool is significant from an educational perspective, offering virtual simulation of interventions and facilitating knowledge sharing among practitioners even at a distance.
The technology could be very useful in guiding inexperienced surgeons during surgeries, creating a virtual operating room with no boundaries and in hard-to-reach settings or emergency situations, enabling the sharing of medical expertise in real time.
“Only by enabling health workers to share their expertise in real time and providing new means of training staff can we tend to close the gap in care between poor and rich countries.” (Ruby)
AR and medicine: sharing standards
In conclusion, interest in AR technologies in medicine by the scientific community and industry has increased significantly.
This is evidenced by the exponential multiplication of scientific publications and startups proposing increasingly advanced prototypes tailored to clinical needs.
Finally, shared guidelines, standards and methodologies are needed to press the accelerator in the development of these technologies.
Fastbrain for public administration
The Public Administrations Electronic Marketplace (MePa) is a digital marketplace where qualified administrations can purchase services and goods offered by suppliers qualified to submit their catalogs on the system.
Fastbrain Engineering S.r.l. is able to offer targeted consulting with a dedicated team for technology investment through the MEPA platform.

We are present on the purchasing portal with a catalog of IT products and a dedicated team, and we act as a technical partner to make choices easier for P.A. purchases by recommending the right item.
About Fastbrain and why to choose it
Fastbrain Engineering Ltd. Certified Partnerof leading Technology Players, including RealWear®, Brother, Lenovo, Synology, Graetz, SiComputer, Canyonoffers customized purchasing solutions tailored to the needs of professionals. It also offers pre- and post-sales support,including operational rental. We are acentralplayer in ICT wholesale distribution and one of the leading players throughout the country in the IT and technology products distribution market. A key feature and competitive advantage is the selection of top brands and leading products in the most popular product categories.
Info:
info@fastbrain.it
| Tel 011.0376.054
Contact us for a free consultation
Sources:
- https://www.scienzedellavita.it/it/meetthelifesciences/7956-chirurgia-condotta-la-prima-operazione-guidata-dalla-realt%C3%A0-aumentata
- https://tech4future.info/realta-aumentata-chirurgia-vantaggi-ar
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6658230/
- https://forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2023/06/01/augmented-reality-is-already-changing-healthcare-for-the-better/
- https://www.scienzedellavita.it/it/meetthelifesciences/8068-la-realt%C3%A0-aumentata-applicata-alla-medicina-lesperienza-di-vostars-guida-la
- *https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10148745/
- https://www.linkiesta.it/2023/02/realta-virtuale-sanita-italia/
- https://www.odontoiatria33.it/approfondimenti/23528/realta-aumentata-in-odontoiatria.html
- https://www.osservatorioterapieavanzate.it/innovazioni-tecnologiche/altre-innovazioni/realta-aumentata-per-studiare-il-cuore-si-passa-dai-libri-allo-smartphone
- https://www.gvmnet.it/press-news/news-dalle-strutture/studio-pre-operatorio-con-la-realta-aumentata
- https://tech4future.info/realta-aumentata-chirurgia-vantaggi-ar/
- https://newsroom.clevelandclinic.org/2019/01/14/cleveland-clinic-using-augmented-reality-to-enhance-liver-cancer-therapy/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10148745/
- https://forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2023/06/01/augmented-reality-is-already-changing-healthcare-for-the-better/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10136227/